Davide Zanetti, Cristian De Luca, and Davide Bonifazi discuss the resurgence of peri-xanthenoxanthene from a forgotten dye into a versatile organic semiconductor and sustainable photocatalyst, emphasizing its importance in photoredox catalysis.
Publications
A bright comeback for peri-xanthenoxanthene
Bottom-up fabrication of BN-doped graphene electrodes from thiol-terminated borazine molecules working in solar cells
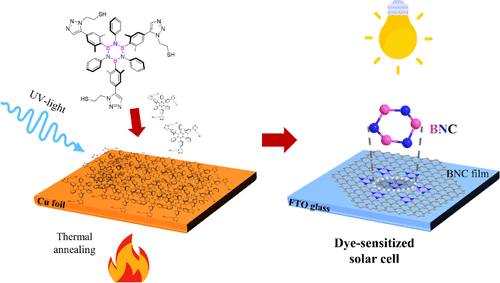
Graphene exhibits exceptional properties, including high tensile strength, mechanical stiffness, and electron mobility. Chemical functionalization of graphene with boron and nitrogen is a powerful strategy for tuning these properties for specific applications. Molecular self-assembly provides an efficient pathway for the tailored synthesis of doped graphene, depending on the molecular precursor used. This study presents a scalable approach to synthesizing large-area boron- and nitrogen-doped graphene using two borazine precursors bearing thiol functionalities. After self-assembly on electropolished polycrystalline copper foil, the precursors undergo photopolymerization under UV irradiation, and subsequent annealing in vacuum transforms the cross-linked BN-doped layer into a graphenoid structure. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy confirms the integration of the borazine rings into the BNC architecture, while Raman spectroscopy reveals a red shift in the characteristic G bands along with intense and broad D bands, highlighting boron–nitrogen contributions. Transmission electron microscopy provides insight into the morphology and structural quality of the BNC films. The BNC films were successfully integrated as counter electrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells, achieving a power conversion efficiency of up to 6% under 1 sun illumination and 11.8% under low-intensity indoor ambient light. Hence, this work not only establishes a straightforward, controllable route for heteroatom doping but also introduces a novel concept of Pt-free counter electrodes for efficient indoor energy harvesting applications.
Catalyst-Transfer Macrocyclization Protocol: Synthesis of π-Conjugated Azaparacyclophanes Made Easy

The present Protocol describes the application of the catalyst-transfer macrocyclization (CTM) reaction, focusing on the synthesis of aza[1n]paracyclophanes (APCs). APCs are fully π-conjugated shape-persistent macrocycles with potential supramolecular chemistry and materials science applications. This method leverages the Pd-catalyzed Buchwald–Hartwig cross-coupling reaction to selectively form π-conjugated cyclic structures, a significant advancement due to its efficiency, versatility, and scalability. Overall, this Article highlights the following attributes of the CTM method: a) Efficiency and Yield: The CTM method works at mild temperatures (40 °C) and short reaction times (≥2 h), producing high yields of APCs (>75% macrocycles). It avoids the typical high-dilution conditions, making it more practical for large-scale applications. b) Versatility: The method allows the synthesis of APCs with diverse endocyclic and exocyclic functionalities and ring sizes (typically from 4- to 9-membered rings), expanding the chemical space for these compounds. This flexibility is crucial for tailoring APC properties for specific applications. c) Scalability and Reproducibility: Unlike many macrocyclization reactions, which require highly dilute conditions, CTM can perform under concentrated regimes (35–350 mM), making it more suitable for large-scale applications. d) Applications in Materials Science: APCs are noted for their potential in optoelectronic applications due to their π-conjugated structures, which are helpful in organic semiconductors, light-harvesting systems, and other advanced materials. This approach addresses the challenge of complicated multistep syntheses that have hindered the widespread integration of APCs into functional devices. A step-by-step guide to preparing exemplary APCs, including troubleshooting, is provided with photographic illustrations.
Combining broadband absorbing electrochromic materials for hybrid grey-to-colourless flexible devices
This study presents a grey-to-colourless hybrid electrochromic device combining a novel red-to-colourless polymer with blue-to-colourless Prussian blue. The device achieves a neutral tint in both the dark and bleached states, with notable changes in visible light transmittance and fast response.
Cyano‐Borazine Photosensitizers for Dye‐Sensitized Solar Cells
Implementing novel metal-free and strongly absorbing donor–acceptorsensitizers without carboxylic acid anchoring groups are still a frontier in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). Herein, the facile synthesis of a strongly absorbingsensitizer combining three 1,1,4,4-tetracyanobuta-1,3-diene (TCBD) anchoringmoieties with a borazine core instead of the classical cyano anchoring groups,such as tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) and tetracyanoethylene (TCNE), andthe dimethyl-phenyl amino donor group, is disclosed. This results in a 1.6-foldincrease in solar energy conversion efficiency compared to DSSCs with thereference sensitizers (TCBD-dimethyl-amino-phenyl core) and the prior art cyano-sensitizers with TCNE and TCNG anchors. The advantages of the TCBD-borazinedesign are twofold: 1) threefold increase in absorption extinction coefficient aswell as 2) a reduction in back electron transfer and aggregation behavior upon dyeadsorption onto the semiconducting electrode, resulting in 45% and 23%improvement in open-circuit voltage (V oc) and short-circuit current density (J sc ),respectively, compared to those of the prior art. Overall, this work highlights aneasy-to-design of cyano-sensitizer that results in a significant improvement ofsolar energy conversion when using borazine frameworks for the first time.
Assessing the energetic and environmental sustainability of organic borazines preparation: A comprehensive life cycle assessment and uncertainty analysis
Since its inception, organic synthesis has played a fundamental role in the development of society, as its efficiency is essential for the preparation of materials in several strategic sectors such as pharmaceuticals, transportation and energy. In this context, organic borazines have emerged as promising molecules useful both as doping units and organic semiconductors, particularly in the production of photovoltaics and organic transistors. However, like most “fine chemical” products, their engineering is generally complex and harmful to the environment due to the need for dangerous reagents, solvents, and harsh reaction conditions. Recent adopted advancements in the manufacturing process, including continuous-flow synthesis and the use of safer, biomass-derived solvents, have been confirmed through a comprehensive cradle-to-gate life cycle assessment (LCA). The study, compared to four batch processes from the literature, identified electricity consumption as the primary contributor to environmental and human health impacts. Additionally, it was demonstrated that adopting a continuous-flow approach, which reduces electricity consumption and leverages safer reaction media such as 2-MeTHF, characterized by an exceptional recovery rate (90%), proved to be an effective strategy, resulting in a notable 11% reduction in emissions. Furthermore, an uncertainty analysis using the Monte Carlo method revealed that energy mixes reliant on fossil fuels increase the impacts across all categories related to human health damage.
Expression of hyperconjugative stereoelectronic interactions in borazines
This paper discusses hyperconjugative stereoelectronic effects in borazines. A series of alkyl-substituted borazines were synthesized and analysed by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Supported by NBO analyses, the significant decreases in 1JCH coupling constant for the CH groups adjacent to the boron atoms are consistent with the presence of and interactions. These interactions lower the electrophilicity of boron atoms, enhancing moisture stability and establishing these molecules as valuable scaffolds in synthetic chemistry and materials science.
Escape from Flatland: Stereoselective Synthesis of Hexa-aryl Borazines and their sp²-Based 3D Architectures
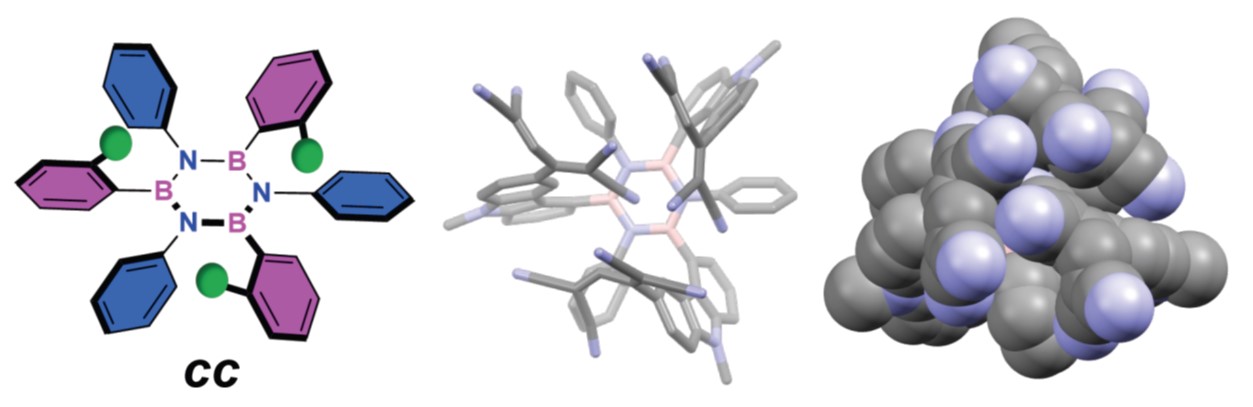
Borazine and its derivatives can be considered critical doping units for engineering hybrid C(sp2)-based molecules with tailored optoelectronic properties. Herein, we report the first synthesis of hexaarylborazines that, bearing ortho-substituted aryl moieties, extend three-dimensionally. Using a one-pot protocol, we first form an electrophilic chloroborazole and then react it with an aryl lithium (ArLi). By selecting the appropriate ortho-substituent, we can guide the ArLi to add to the BN-core in a specific way, ultimately controlling the stereochemical outcome of the three-substitution reaction. Rationalization of the stereochemical model through computational analysis allowed us to show that when aryl lithium nucleophiles bearing rigid long-range ortho-substituents are used, i.e., stiff substituents. The ortho-substituent shields its side of the electrophilic B3N3 core, biasing the incoming ArLi to add anti at each addition step, forming the final tri-aryl borazine exclusively as cc-isomer. Leveraging this stereoselective approach, prototypical multichromophoric borazine derivatives were prepared, and we showcased how the stereochemical arrangement of these chromophores distinctly influences their redox behavior. This methodology paves the way for previously inaccessible borazines to serve as privileged precursors to transcend the conventional bidimensionality associated with graphenoid systems and pioneer the construction of new forms of three-dimensional C(sp2)-based architectures.
Long-range supramolecular assembly of a pyrene-derivatized polythiophene/MWCNT hybrid for resilient flexible electrochromic displays
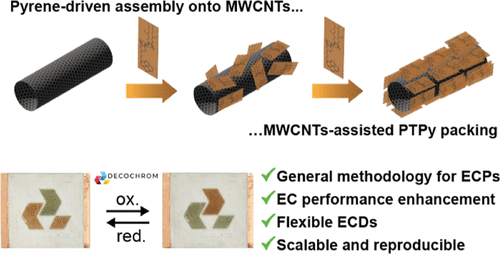
Organic electrochromic polymers hold great potential for integration into low-power flexible electrochromic displays (F-ECDs) due to their wide range of colors and simple processing. However, challenges such as inefficient charge transfer and degradation upon device integration hinder their practical applications. Herein, we report an innovative, general approach that utilizes template-induced supramolecular nanostructuring to engineer established electrochromic polymers, enhancing their performance and durability. We modified a well-known, albeit underperforming in F-ECDs, poly-thiophene polymer (ECP Orange; PT) by incorporating a pyrene appendage, resulting in a copolymer (PTPy) capable of undergoing large-scale assembly in the presence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), driven by the establishment of π–π interactions between the pyrene and the MWCNTs (PTPy/MWCNTs). F-ECDs based on these hybrids, produced by spray coating, exhibit improved color switching speeds (t90OX = 3.6 s, t90RED = 0.3 s) compared to those of the PT polymer (t90OX = 53.2 s, t90RED = 2.5 s). Additionally, PTPy/MWCNTs F-ECDs demonstrate longer cyclability (half-life based on ΔE, ΔE50% = 17.6k cycles) compared to PT (ΔE50% = 278 cycles), also when blended with MWCNTs (ΔE50% = 282 cycles). This work highlights the pivotal role of engineered supramolecular nanostructuring in boosting the performance of organic electrochromic materials, making them suitable for F-ECD scalable commercial applications.
Hybrid Screen Printable Electrolyte for Large-Scale Flexible Electrochromic Display Production
This study presents the development of a novel screen printable quasi-solid polymer electrolyte (p-QSPE) for Electrochromic Displays (ECDs) applications. p-QSPE is composed of three key components: polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), a high-dielectric constant polymer that ensures high ionic conductivity in solid-state; glyceril propoxy triacrylate (GPTA), a UV-cross-linkable monomer that provides structure and durability for overprinting; titanium dioxide (TiO₂) nanoparticles, which modulate the electrolyte’s rheological properties for screen printing; reducing the solvent (PC:EC) content to only 35.90 wt.%. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) revealed that this well-designed formulation achieved an ionic conductivity of 1.17 × 10−3 S cm−1 at room temperature, surpassing the threshold required for commercial applications. Moreover, p-QSPE facilitated the production of fully screen printed ECDs in an industrial printing line, streamlining their production process and achieving an optimal balance between printability, overprint resilience, and device performance. Operational tests for the ECDs showed fast switching times (<6 s for t90 and <2 s for t75) across a wide temperature range (−20 °C to 80 °C). Additionally, the electrolyte demonstrated low charge consumption (2.10 ± 0.11 mC cm−2) and a lifespan exceeding 10 000 cycles. These results highlight the potential of p-QSPE as a screen printable, high-performance electrolyte, capable of advancing ECD manufacturing by enabling the production of fully screen-printed, performing ECDs.
Surface Chemistry of a Halogenated Borazine: From Supramolecular Assemblies to a Random Covalent BN‐Substituted Carbon Network
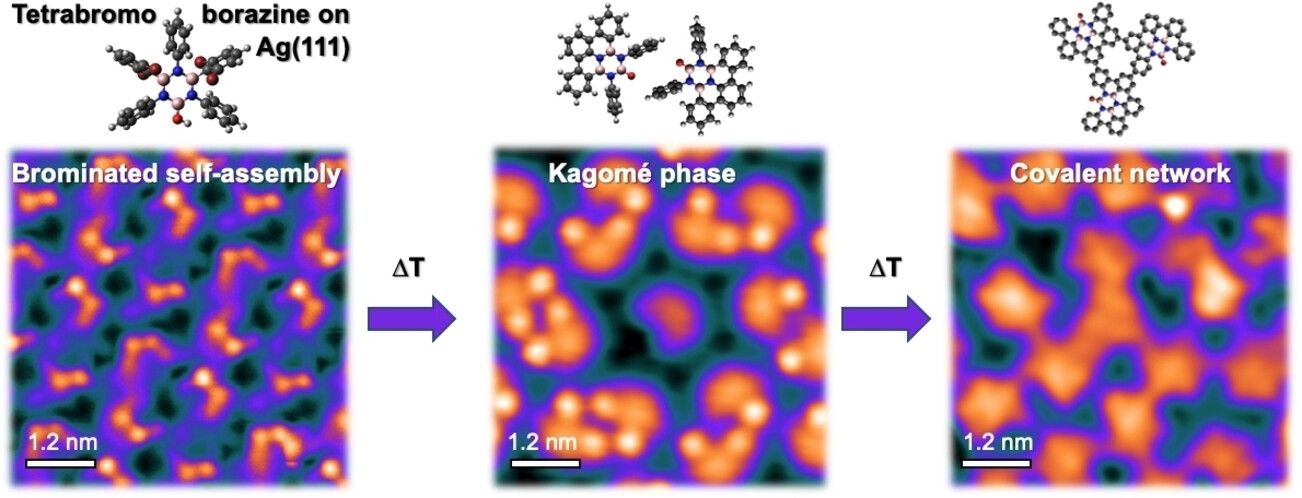
The on‐surface synthesis strategy has emerged as a promising route for fabricating well‐defined two‐dimensional (2D) BN‐substituted carbon nanomaterials with tunable electronic properties. This approach relies on specially designed precursors and requires a thorough understanding of the on‐surface reaction pathways. It promises precise structural control at the atomic scale, thus complementing chemical vapor deposition (CVD). In this study, we investigated a novel heteroatomic precursor, tetrabromoborazine, which incorporates a BN core and an OH group, on Ag(111) using low temperature scanning tunnelling microscopy/spectroscopy (LT‐STM/STS) and X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Through sequential temperature‐induced reactions involving dehalogenation and dehydrogenation, distinct tetrabromoborazine derivatives were produced as reaction intermediates, leading to the formation of specific self-assemblies. Notably, the resulting intricate supramolecular structures include a chiral kagomé lattice composed of molecular dimers exhibiting a unique electronic signature. The final product obtained was a random covalent carbon network with BN-substitution and embedded oxygen heteroatoms. Our study offers valuable insights into the significance of the structure and functionalization of BN precursors in temperature-induced on-surface reactions, which can help future rational precursor design. Additionally, it introduces complex surface architectures that offer a high areal density of borazine cores.
Solution Versus On-Surface Synthesis of Peripherally Oxygen-Annulated Porphyrins through C−O Bond Formation
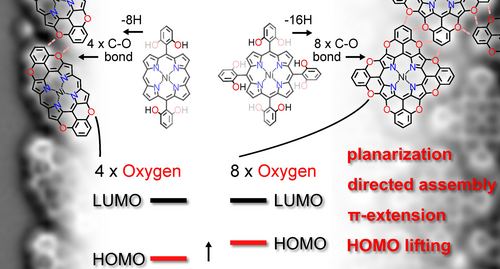
This study investigates the synthesis of tetra- and octa-O-fused porphyrinoids employing an oxidative O-annulation approach through C−H activation. Despite encountering challenges such as overoxidation and instability in conventional solution protocols, successful synthesis was achieved on Au(111) surfaces under ultra-high vacuum (UHV) conditions. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, scanning tunneling microscopy, and non-contact atomic force microscopy elucidated the preferential formation of pyran moieties via C−O bond formation and subsequent self-assembly driven by C−H⋅⋅⋅O interactions. Furthermore, the O-annulation process was found to reduce the HOMO–LUMO gap by lifting the HOMO energy level, with the effect rising upon increasing the number of embedded O-atoms.
Double Chalcogen Bonding Recognition Arrays in Solution
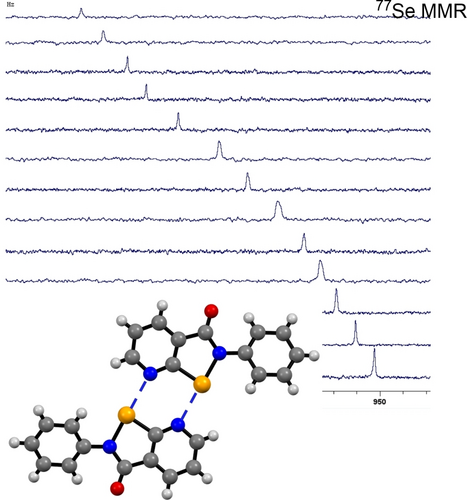
N-substituted pyridino-based congeners of Ebselen, named here as Pyrselen, incorporating proximal Se and N atoms, undergo dimerization in solution and the solid state through a dual donor-acceptor arrangement of chalcogen bonding sites. Dimerization constants were measured within the 5–50 M−1 range. Computational studies on the dimers depict a notable charge-transfer contribution to the association, validating Pyrselen as an effective scaffold for designing chalcogen-bonding-based recognition motifs.
One-Step Catalyst-Transfer Macrocyclization: Expanding the Chemical Space of Azaparacyclophanes
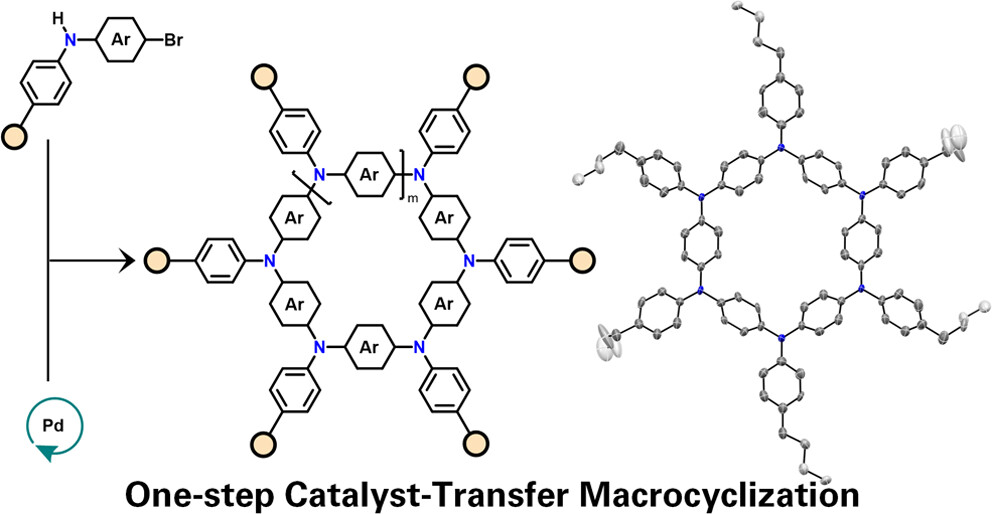
In this paper, we report on a one-step catalyst-transfer macrocyclization (CTM) reaction, based on the Pd-catalyzed Buchwald-Hartwig cross-coupling reaction, selectively affording only cyclic structures. This route offers a versatile and efficient approach to synthesize aza[1(n)]paracyclophanes (APCs) featuring diverse functionalities and lumens. The method operates at mild reaction temperatures (40 degrees C) and short reaction times (similar to 2 h), delivering excellent isolated yields (>75% macrocycles) and up to 30% of a 6-membered cyclophane, all under nonhigh-dilution concentrations (35-350 mM). Structural insights into APCs reveal variations in product distribution based on different endocyclic substituents, with steric properties of exocyclic substituents having minimal influence on the macrocyclization. Aryl-type endocyclic substituents predominantly yield 6-membered macrocycles, while polycyclic aromatic units such as fluorene and carbazole favor 4-membered species. Experimental and computational studies support a proposed mechanism of ring-walking catalyst transfer that promotes the macrocycle formation. It has been found that the macrocyclization is driven by the formation of cyclic conformers during the oligomerization step favoring an intramolecular C-N bond formation that, depending on the cycle size, hinges on either preorganization effect or kinetic increase of the reductive elimination step or a combination of the two. The CTM process exhibits a living behavior, facilitating sequential synthesis of other macrocycles by introducing relevant monomers, thus providing a practical synthetic platform for chemical libraries. Notably, CTM operates both under diluted and concentrated regimes, offering scalability potential, unlike typical macrocyclization reactions usually operating in the 0.1-1 mM range.
On-Surface Molecular Recognition Driven by Chalcogen Bonding
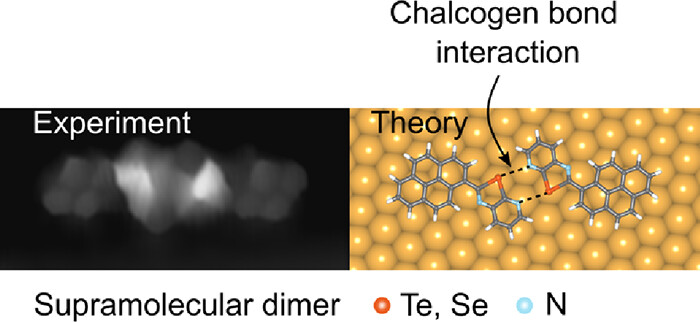
Chalcogen bonding interactions (ChBIs) have been widely employed to create ordered noncovalent assemblies in solids and liquids. Yet, their ability to engineer molecular self-assembly on surfaces has not been demonstrated. Here, we report the first demonstration of on-surface molecular recognition solely governed by ChBIs. Scanning tunneling microscopy and ab initio calculations reveal that a pyrenyl derivative can undergo noncovalent chiral dimerization on the Au(111) surface through double ChN interactions involving Te- or Se-containing chalcogenazolo pyridine motifs. In contrast, reference chalcogenazole counterparts lacking the pyridyl moiety fail to form regular self-assemblies on Au, resulting in disordered assemblies.
Celebrating Maurizio Prato’s Passion, Talent and Imagination.

You may say I am a dreamer” (Imagine, John Lennon, 1971)
Scientific imagination is a very unique status of mind, the place where new ideas are forged, the very first nucleus of outstanding and surprising discoveries. As such, this is by no means a random idea generator or a casual collection of weakly bonded thoughts. It takes much more to turn a“dreamer” into a visionary scientist. This capacity is rare, as it requires deep commitment, sharp focus, and strong resilience, together with disruptive and contagious creativity, tempered by calm and positive strength, empathy, thoughtfulness, and, above all, empowered by a generous attitude towards opening spaces for collaborative leadership. It takes a whole team to Tango in Science, orchestrated in one cooperative harmony, where every voice of the team members is valued within a full orchestra, tuned to beat at the same rhythm of collaboration. This editorial introduces a Special Collection of papers in honor of Maurizio Prato, showcasing prominent examples of his team‘s work in harmonizing frontier research complexity with groundbreaking achievements in the field of carbon nanostructures (CNS) and molecular nanosciences. The Prato group has established a unique way of playing a broad interdisciplinary research role, tuned at the rhythm of passion and creativity, merging organic and inorganic synthesis with supramolecular chemistry, bioinspired nano-systems, and materials science. Here, the spotlight is on the legacy of Maurizio Prato, listening to the sound of science,being aware of each contribution asolo, but sharing the harmony, strengthening motivation and intensity, making an impact, having fun, and enjoying the melody. Throughout this journey, Maurizio Prato has been considered as one of the most influential scientists for the design and synthesis of tailored CNS as biosustainable functional materials with applications in regenerative medicine and in solar energy research.The Special Collection honors Maurizio Prato with a series of rich contributions highlighting a broad spectrum of research themes that in many ways acknowledge his scientific influence. We encourage the readers to find their ’swing’ in this narrative, taking inspiration for opening new projects and perspectives.
Photoredox Annulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
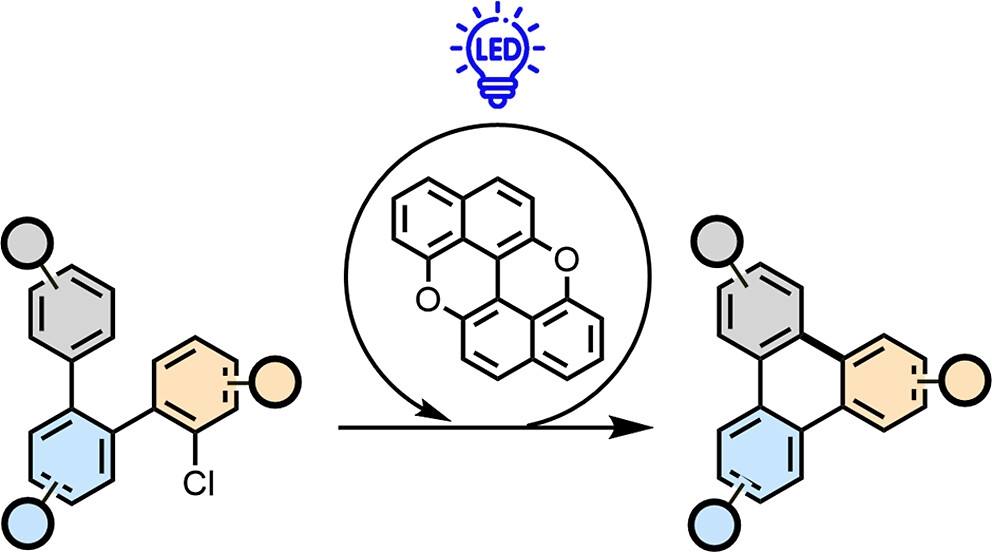
The rise of interest in using polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and molecular graphenoids in optoelectronics has recently stimulated the growth of modern synthetic methodologies giving access to intramolecular aryl-aryl couplings. Here, we show that a radical-based annulation protocol allows expansion of the planarization approaches to prepare functionalized molecular graphenoids. The enabler of this reaction is peri-xanthenoxanthene, the photocatalyst which undergoes photoinduced single electron transfer with an ortho-oligoarylenyl precursor bearing electron-withdrawing and nucleofuge groups. Dissociative electron transfer enables the formation of persistent aryl radical intermediates, the latter undergoing intramolecular C-C bond formation, allowing the planarization reaction to occur. The reaction conditions are mild and compatible with various electron-withdrawing and -donating substituents on the aryl rings as well as heterocycles and PAHs. The method could be applied to induce double annulation reactions, allowing the synthesis of pi-extended scaffolds with different edge peripheries.
Photoreduction of Anthracenes Catalyzed by peri-Xanthenoxanthene: a Scalable and Sustainable Birch-Type Alternative
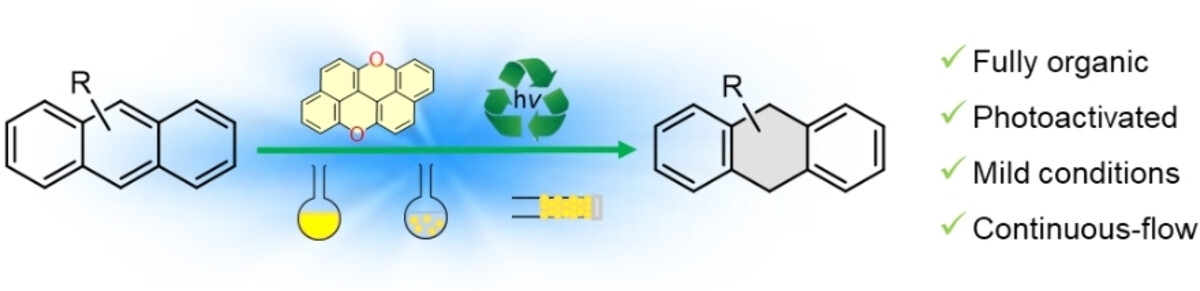
The typical Birch reduction transforms arenes into cyclohexa-1,4-dienes by using alkali metals, an alcohol as a proton source, and an amine as solvent. Capitalizing on the strong photoreductive properties of peri-xanthenoxanthene (PXX), herein we report the photocatalyzed Birch-type reduction of acenes by employing visible blue light irradiation at room temperature in the presence of air. Upon excitation at 405 or 460 nm in the presence of a mixture of N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) and trifluoromethanesulfonimide (HNTf2) in DMSO, PXX photocatalyzes the selective reduction of full-carbon acene derivatives (24-75 %). Immobilization of PXX onto polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) beads (PXX-PDMS) allowed the use of the catalyst in heterogeneous batch reactions, giving 9-phenyl-9,10-dihydroanthracene in high yield (68 %). The catalyst could easily be recovered and reused, with no notable drop in performance observed after five reaction cycles. Integration of the PXX-PDMS beads into a microreactor enabled the reduction of acenes under continuous-flow conditions, thereby validating the sustainability and scalability of this heterogeneous-phase approach.
Indacaterol inhibits collective cell migration and IGDQ-mediated single cell migration in metastatic breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells

Metastasis is the main cause of deaths related to breast cancer. This is particular the case for triple negative breast cancer. No targeted therapies are reported as efficient until now. The extracellular matrix, in particular the fibronectin type I motif IGDQ, plays a major role in regulating cell migration prior metastasis formation. This motif interacts with specific integrins inducing their activation and the migratory signal transduction.Here, we characterized the migratory phenotype of MDA-MB-231 cells, using functionalized IGDQ-exposing surfaces, and compared it to integrin A5 and integrin B3 knock-down cells. A multiomic analysis was developed that highlighted the splicing factor SRSF6 as a putative master regulator of cell migration and of integrin intracellular trafficking. Indacaterol-induced inhibition of SRSF6 provoked: i) the inhibition of collective and IGDQ-mediated cell migration and ii) ITGA5 sequestration into endosomes and lysosomes. Upon further studies, indacaterol may be a potential therapy to prevent cell migration and reduce metastasis formation in breast cancer.1CRnmBvVXp9LXQy1nJKbUFVideo Abstract
Tweaking the Optoelectronic Properties of S-Doped Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Chemical Oxidation
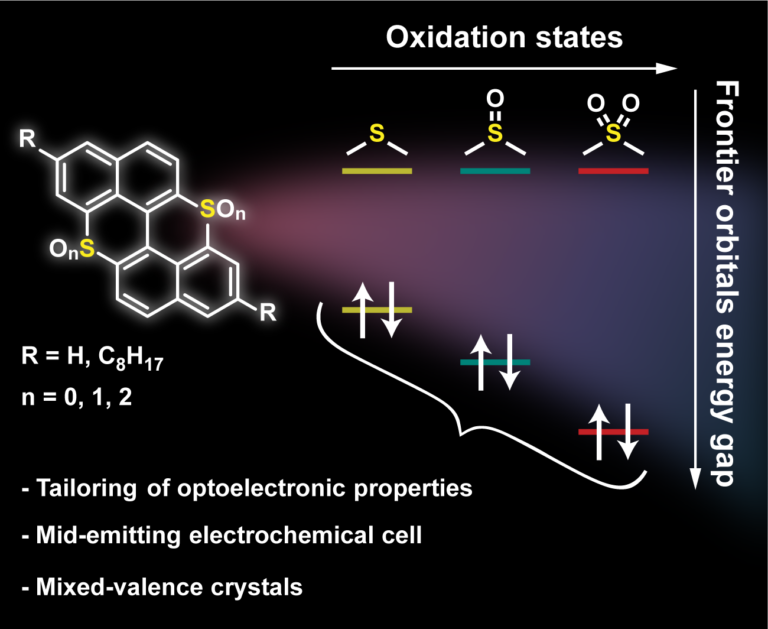
Peri-thiaxanthenothiaxanthene, an S-doped analog of peri-xanthenoxanthene, is used as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) scaffold to tune the molecular semiconductor properties by editing the oxidation state of the S-atoms. Chemical oxidation of peri-thiaxanthenothiaxanthene with H2O2 led to the relevant sulfoxide and sulfone congeners, whereas electrooxidation gave access to sulfonium-type derivatives forming crystalline mixed valence (MV) complexes. These complexes depicted peculiar molecular and solid-state arrangements with face-to-face pi-pi stacking organization. Photophysical studies showed a widening of the optical bandgap upon progressive oxidation of the S-atoms, with the bis-sulfone derivative displaying the largest value (E-00=2.99 eV). While peri-thiaxanthenothiaxanthene showed reversible oxidation properties, the sulfoxide and sulfone derivatives mainly showed reductive events, corroborating their n-type properties. Electric measurements of single crystals of the MV complexes exhibited a semiconducting behavior with a remarkably high conductivity at room temperature (10(-1)-10(-2) S cm(-1) and 10(-2)-10(-3) S cm(-1) for the O and S derivatives, respectively), one of the highest reported so far. Finally, the electroluminescence properties of the complexes were tested in light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs), obtaining the first S-doped mid-emitting PAH-based LECs.
Engineering Te-Containing Recognition Modules for Chalcogen Bonding: Towards Supramolecular Polymeric Materials
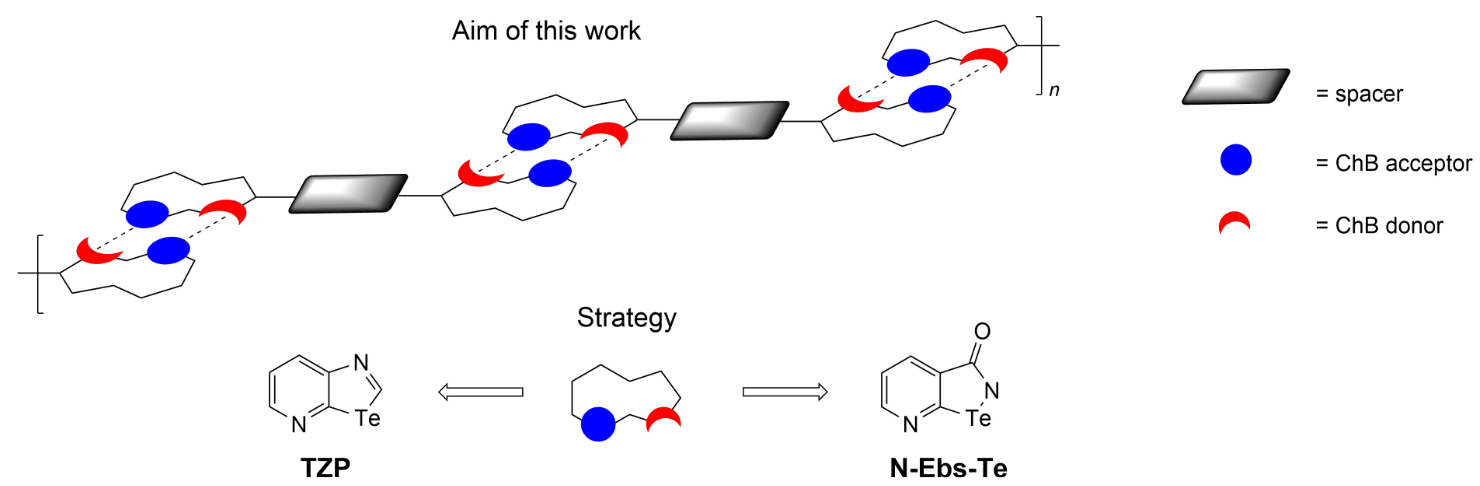
Aiming at the preparation of one-dimensional (1D) chalcogen-bonded supramolecular polymers at the solid state, this work describes the different syntheses which have been challenged to obtain ditopic molecular modules. At first, tellurazolopyridyl (TZP) rings have been chosen as recognition units, given their well-proven ability and persistency to self-assemble through double Te center dot center dot center dot N chalcogen bonds (ChBs). The second synthetic strategy dealt with the preparation of pyridyl-modified ebselen Te-containing analogues. By attempting several synthetic protocols, the targeted ebselen derivatives could not be obtained, whereas an unexpected Te-containing lactone as well as a spiro-type Te(IV)-containing derivatives were isolated, with the latter investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis.
Expanding the Library of 2-Phenylbenzotellurazoles: Red-Shifting Effect of Ethoxy Functionalities on the UV/Vis Absorption Properties
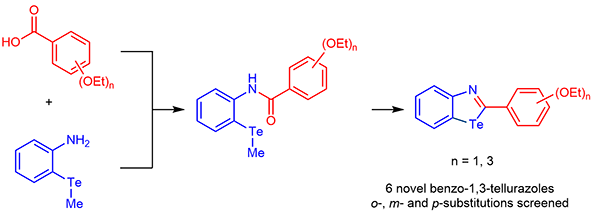
This work describes the high-yield synthesis of a novel series of benzotellurazoles bearing a phenyl ring in 2-position, which is differently functionalized with ethoxy chains. Changing the number and the position of these functional groups determines differences in the self-assembly in the solid state, as well as in the photophysical properties of the targeted molecules. As anticipated by theoretical calculations of the HOMO-LUMO gap of each molecule, the presence of ethoxy chains in nand p-positions determines up to 20 nm red-shifts in the absorption peaks, when compared to unsubstituted benzotellurazole. Similarly, more significant changes are observed in the chemical shifts of Te-125 NMR spectra for those derivatives bearing o- and p-ethoxy functionalization.
Boron Nitride-Doped Polyphenylenic Organogels
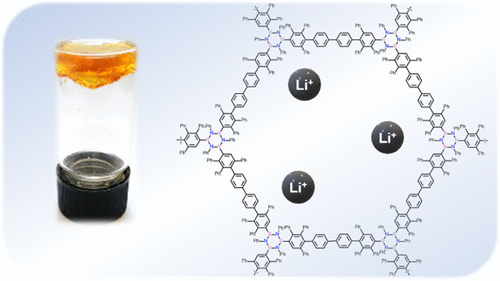
Herein, we describe the synthesis of the first boron nitride-doped polyphenylenic material obtained through a [4 + 2] cycloaddition reaction between a triethynyl borazine unit and a biscyclopentadienone derivative, which undergoes organogel formation in chlorinated solvents (the critical jellification concentration is 4% w/w in CHCl3). The polymer has been characterized extensively by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, solid-state C-13 NMR, solid-state B-11 NMR, and by comparison with the isolated monomeric unit. Furthermore, the polymer gels formed in chlorinated solvents have been thoroughly characterized and studied, showing rheological properties comparable to those of polyacrylaniide gels with a low crosslinker percentage. Given the thermal and chemical stability, the material was studied as a potential support for solid-state electrolytes. showing properties comparable to those of polyethylene glycol-based electrolytes, thus presenting great potential for the application of this new class of material in lithium-ion batteries.
HOMO Energy-Level Lifting in p-Type O-Doped Graphenoids: Synthesis of Electrochromic Alkoxy-Decorated Xanthenoxanthenes
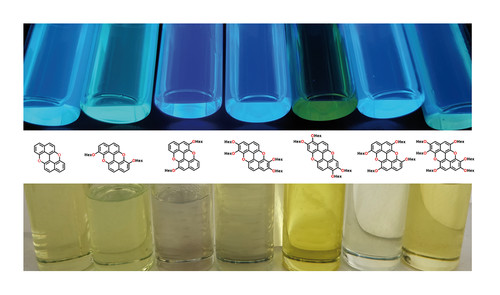
A series of novel O-doped polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, bearing a different number of electron-donating alkoxy substituents, has been prepared using a novel copper-promoted anaerobic protocol for the cyclisation of highly electron rich peri-xanthenoxanthene molecular modules. The effect of the number and position of the alkoxy substituents on the optoelectronic properties has thus been investigated, unveiling p-type semiconducting properties. All molecules displayed a significant colour change upon oxidation, suggesting that these compounds can be used to devise chromogenic materials to engineer electrochromic devices.
peri-Acenoacene Ribbons with Zigzag BN-Doped Peripheries
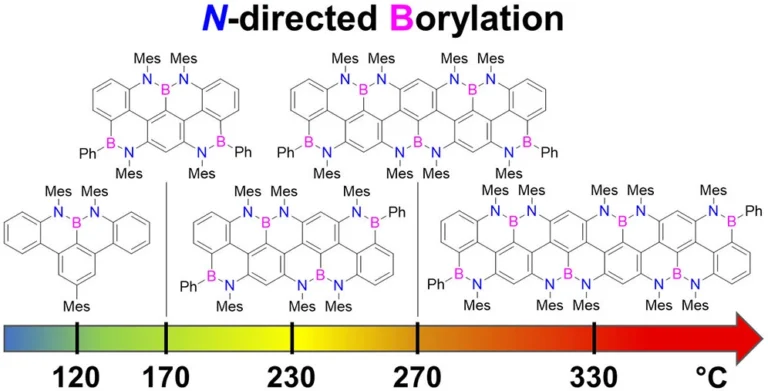
Here, we report the synthesis of BN-doped graphenoid nanoribbons, in which peripheral carbon atoms at the zigzag edges have been selectively replaced by boron and nitrogen atoms as BN and NBN motifs. This includes high-yielding ring closure key steps that, through N-directed borylation reaction using solely BBr3, allow the planarization of meta-oligoarylenyl precursors, through the formation of B-N and B-C bonds, to give ter-, quater-, quinque-, and sexi-arylenyl nanoribbons. X-ray single-crystal diffraction studies confirmed the formation of the BN and NBN motifs and the zigzag-edged topology of the regularly doped ribbons. Steady-state absorption and emission investigations at room temperature showed a systematic bathochromic shift of the UV-vis absorption and emission envelopes upon elongation of the oligoarylenyl backbone, with the nanoribbon emission featuring a TADF component. All derivatives displayed phosphorescence at 77 K. Electrochemical studies showed that the pi-extension of the peri-acenoacene framework provokes a lowering of the first oxidative event (from 0.83 to 0.40 V), making these nanoribbons optimal candidates to engineer p-type organic semiconductors.
Supramolecular Chalcogen-Bonded Semiconducting Nanoribbons at Work in Lighting Devices

This work describes the design and synthesis of a pi-conjugated telluro[3,2-beta][1]-tellurophene-based synthon that, embodying pyridyl and haloaryl chalcogen-bonding acceptors, self-assembles into nanoribbons through chalcogen bonds. The ribbons pi-stack in a multi-layered architecture both in single crystals and thin films. Theoretical studies of the electronic states of chalcogen-bonded material showed the presence of a local charge density between Te and N atoms. OTFT-based charge transport measurements showed hole-transport properties for this material. Its integration as a p-type semiconductor in multi-layered Cu-I-based light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs) led to a 10-fold increase in stability (38 h vs. 3 h) compared to single-layered devices. Finally, using the reference tellurotellurophene congener bearing a C-H group instead of the pyridyl N atom, a herringbone solid-state assembly is formed without charge transport features, resulting in LECs with poor stabilities (<1 h).
IGDQ motogenic peptide gradient induces directional cell migration through integrin ( ?v)?3 activation in MDA-MB-231 metastatic breast cancer cells *
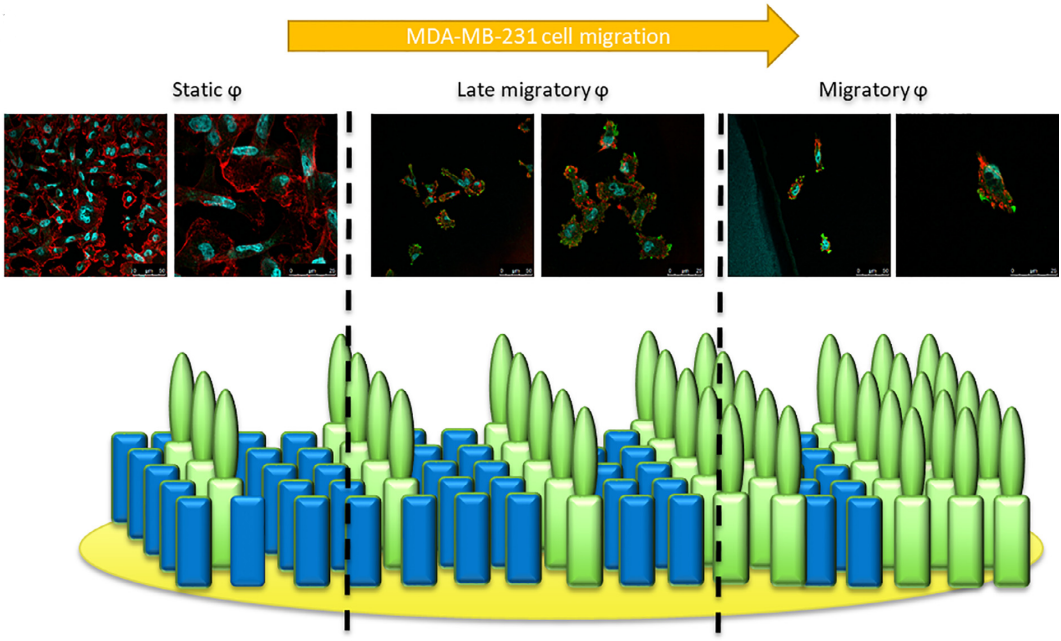
In the context of breast cancer metastasis study, we have shown in an in vitro model of cell migration that IGDQ-exposing (IsoLeuGly-Asp-Glutamine type I Fibronectin motif ) monolayers (SAMs) on gold sustain the adhesion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by triggering Focal Adhesion Kinase and integrin activation. Such tunable scaffolds are used to mimic the tumor extracellular environment, inducing and controlling cell migration. The observed migratory behavior induced by the IGDQ-bearing peptide gradient along the surface allows to separate cell subpopulations with a stationary or migratory phenotype. In this work, we knocked down the integrins alpha 5( beta 1) and ( alpha v) beta since they are already known to be implicated in cell migration. To this aim, a whole proteomic analysis was performed in beta 3 integrin (ITGB3) or alpha 5 integrin (ITGA5) knock-down MDA-MB-231 cells, in order to highlight the pathways implied in the integrin-dependent cell migration. Our results showed that i) ITGB3 depletion influenced ITGA5 mRNA expression, ii) ITGB3 and ITGA5 were both necessary for IGDQ-mediated directional single cell migration and iii) integrin ( alpha v) beta 3 was activated by IGDQ fibronectin type I motif. Finally, the proteomic analysis suggested that co-regulation of recycling transport of ITGB3 by ITGA5 is potentially necessary for directional